- Getting Started
- Hardware
- Bricks
- Bricklets
- Master Extensions
- Power Supplies
- Discontinued Products
- Bricks
- Bricklets
- Accelerometer Bricklet
- Ambient Light Bricklet
- Ambient Light Bricklet 2.0
- Analog In Bricklet
- Analog In Bricklet 2.0
- Analog Out Bricklet
- CO2 Bricklet
- Current12 Bricklet
- Current25 Bricklet
- Distance US Bricklet
- Dual Button Bricklet
- Dual Relay Bricklet
- GPS Bricklet
- Humidity Bricklet
- Industrial Analog Out Bricklet
- Industrial Digital In 4 Bricklet
- Industrial Dual Analog In Bricklet
- Industrial Quad Relay Bricklet
- IO-4 Bricklet
- Laser Range Finder Bricklet
- LCD 16x2 Bricklet
- LED Strip Bricklet
- Load Cell Bricklet
- Moisture Bricklet
- Motion Detector Bricklet
- NFC/RFID Bricklet
- OLED 128x64 Bricklet
- Piezo Buzzer Bricklet
- PTC Bricklet
- PTC Bricklet 2.0
- Remote Switch Bricklet
- RGB LED Bricklet
- RGB LED Matrix Bricklet
- Rotary Encoder Bricklet
- Solid State Relay Bricklet
- Temperature IR Bricklet
- Thermocouple Bricklet
- UV Light Bricklet
- Voltage Bricklet
- Voltage/Current Bricklet
- Master Extensions
- Timeline
- Software
- Kits
- Embedded Boards
- Specifications
Rotary Encoder Bricklet¶
Note
The Rotary Encoder Bricklet is discontinued and is no longer sold. The Rotary Encoder Bricklet 2.0 is the recommended replacement.
Features¶
- 360° rotary encoder
- Counts 24 steps per rotation (step angle 15°)
- Integrated push-button
Description¶
The Rotary Encoder Bricklet extends Bricks and is equipped with a 360° rotary encoder. It has 24 steps per rotation with a nice clicking feel. The encoder has an integrated push-button (by pressing on the knob) that can be used to select a menu item or similar.
The difference between the Rotary Poti Bricklet and the Rotary Encoder Bricklet is that the encoder has full rotation without limits.
Technical Specifications¶
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Current Consumption | 1mA |
| Number of Steps per Rotation | 24 (step angle 15°) |
| Maximum Number of Steps detectable | up to 250 steps / second |
| Button Operating Force | 200gf |
| Button Travel Distance | 0.5mm |
| Dimensions (W x D x H) | 30 x 25 x 23mm (1.18 x 0.98 x 0.9")* |
| Weight | 5g* |
* without knob
Resources¶
Test your Rotary Encoder Bricklet¶
To test a Rotary Encoder Bricklet you need to have Brick Daemon and Brick Viewer installed. Brick Daemon acts as a proxy between the USB interface of the Bricks and the API bindings. Brick Viewer connects to Brick Daemon. It helps to figure out basic information about the connected Bricks and Bricklets and allows to test them.
Connect the Rotary Encoder Bricklet to a Brick with a Bricklet Cable.
If you connect the Brick to the PC over USB, you should see a new tab named "Rotary Encoder Bricklet" in the Brick Viewer after a moment. Select this tab. If everything went as expected you can now turn the encoder and see the corresponding count.

After this test you can go on with writing your own application. See the Programming Interface section for the API of the Rotary Encoder Bricklet and examples in different programming languages.
Case¶
A laser-cut case for the Rotary Encoder Bricklet is available.

The assembly is easiest if you follow the following steps:
- Screw spacers to the Bricklet,
- screw bottom plate to bottom spacers,
- build up side plates,
- plug side plates into bottom plate and
- screw top plate to top spacers.
Below you can see an exploded assembly drawing of the Rotary Encoder Bricklet case:
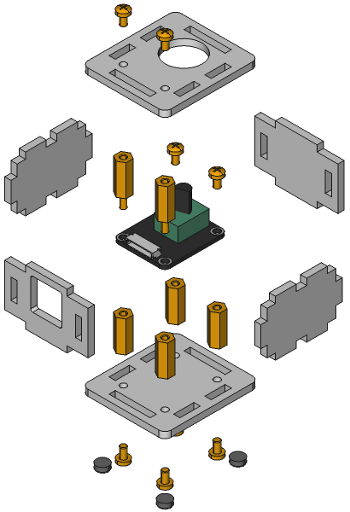
Hint: There is a protective film on both sides of the plates, you have to remove it before assembly.
Programming Interface¶
See Programming Interface for a detailed description.
| Language | API | Examples | Installation |
|---|---|---|---|
| C/C++ | API | Examples | Installation |
| C# | API | Examples | Installation |
| Delphi/Lazarus | API | Examples | Installation |
| Go | API | Examples | Installation |
| Java | API | Examples | Installation |
| JavaScript | API | Examples | Installation |
| LabVIEW | API | Examples | Installation |
| Mathematica | API | Examples | Installation |
| MATLAB/Octave | API | Examples | Installation |
| MQTT | API | Examples | Installation |
| openHAB | API | Examples | Installation |
| Perl | API | Examples | Installation |
| PHP | API | Examples | Installation |
| Python | API | Examples | Installation |
| Ruby | API | Examples | Installation |
| Rust | API | Examples | Installation |
| Shell | API | Examples | Installation |
| Visual Basic .NET | API | Examples | Installation |
| TCP/IP | API | ||
| Modbus | API |










